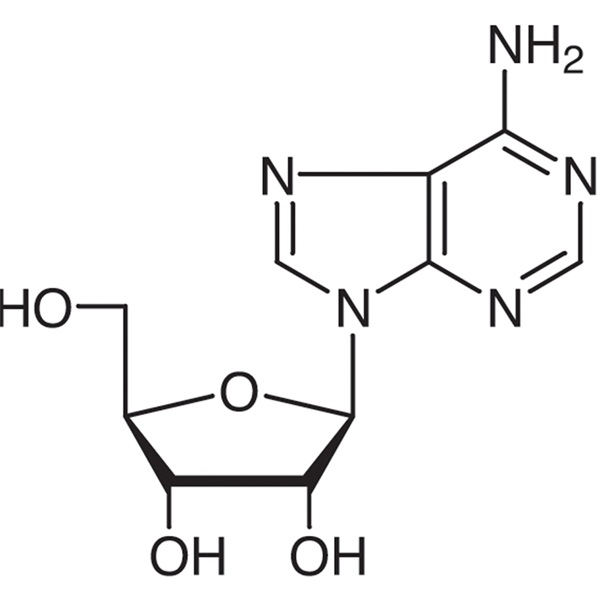
Adenosine CAS 58-61-7 Assay 99.0%-101.0% USP Standard Factory High Purity
Shanghai Ruifu Chemical Co., Ltd. is the leading manufacturer and supplier of Adenosine (CAS: 58-61-7) with high quality, meets with the USP standard, AJI97 standard. Ruifu Chemical supplys a series of Nucleosides, Nucleotides, Nucleic Acids. We can provide worldwide delivery, small and bulk quantities available. If you are interested in Adenosine (CAS: 58-61-7), Please contact: alvin@ruifuchem.com
| Name | Adenosine |
| Synonyms | D-Adenosine; Adenosine, Free Base; Adenocard; Adenine Riboside; 9-beta-D-Ribofuranosyladenine; 9-β-D-Ribofuranosyladenine; 6-Amino-9β-D-Ribofuranosyl-9H-Purine; 6-Amino-9(β-D-Ribofuranosyl)-9H-Purine; Adenine-9-beta-D-Ribofuranoside |
| CAS Number | 58-61-7 |
| Stock Status | In Stock, Production Capacity 500 Tons per Year |
| Molecular Formula | C10H13N5O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 267.25 |
| Melting Point | 233.0~238.0℃ |
| Sensitive | Air Sensitive |
| Solubility | Slightly Soluble in Water, Soluble in Hot Water, Practically Insoluble in Ethanol (96 percent) and in Methylene Chloride |
| Solubility in Hot Water | Almost Transparency |
| Classification | Nucleosides, Nucleotides, Nucleic Acids |
| Brand | Ruifu Chemical |
| Risk Statements | 36/37/38 | F | 10-23 |
| Safety Statements | 24/25-36/37/39-26 | TSCA | Yes |
| WGK Germany | 2 | HS Code | 2934993090 |
| RTECS | AU7175000 | Toxicity | LD50 oral in mouse: > 20gm/kg |
|
Items |
Inspection Standards |
Results |
|
Appearance |
White Crystalline Powder, Odorless |
Complies |
|
Identification |
IR Conforms to the Reference |
Complies |
|
Specific Rotation [a]20/D |
-68.0°~-72.0° (C=2 in 5% NaOH) |
-71.7° |
|
Melting Point |
233.0~238.0℃ |
235.0~236.0℃ |
|
Acidity or Alkalinity |
Meets the Requirements |
Complies |
|
Loss on Drying |
≤0.50% |
0.04% |
|
Heavy Metals |
≤10ppm |
<10ppm |
|
Residue on Ignition |
≤0.10% |
0.08% |
|
Limit of Ammonia |
≤0.0004% |
<0.0004% |
|
Limit of Chloride |
≤0.007% |
<0.007% |
|
Limit of Sulfate |
≤0.02% |
<0.02% |
|
Guanosine |
≤0.10% |
Absence |
|
Insine |
≤0.10% |
0.01% |
|
Uridine |
≤0.10% |
Absence |
|
Adenine |
≤0.10% |
Absence |
|
Total Impurities |
≤0.50% |
0.03% |
|
Assay |
99.0~101.0% (on the dried basis) |
100.3% |
|
Test Standard |
USP35 Standard |
Complies |
|
Downstream Products |
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP), Adenine, Adenylate, Adenosine Arabinose | |
Package: Bottle, Aluminum foil bag, 25kg/Cardboard Drum, or according to customer's requirement.
Storage Condition: Store in sealed containers at cool and dry place; Protect from light, moisture. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents.
DEFINITION
Adenosine contains NLT 99.0% and NMT 101.0% of C10H13N5O4, calculated on the dried basis.
IDENTIFICATION
• A. INFRARED ABSORPTION <197K>: NMT 0.1%
ASSAY
• ADENOSINE
Sample: 200 mg of Adenosine previously dried at 105° for 2h
Titrimetric system
(See Titrimetry <541>)
Mode: Direct titration
Titrant: 0.1 N per chloric acid VS
Endpoint detection: Potentiometric
Analysis: Dissolve in 50 mL of glacial acetic acid and titrate with 0.1 N per chloric acid VS. Calculate the per centage of Adenosine (C10H13N5O4) in the portion taken:
Result = [(V − B) × N × F × 100]/W
V = Sample titrant volume (mL)
B = Blank titrant volume (mL)
N= titrant normality (mEq/mL)
F= equivalency factor: 267.25 mg/mEq
W= weight of the Sample (mg)
Acceptance criteria: 99.0%-101.0% on the dried basis
• IMPURITIES
• RESIDUEON IGNITION <281>: NMT 0.1%
• HEAVY METALS, Method II <231>: NMT 10 ppm
• LIMIT OF AMMONIA
Sample solution: Suspend 0.5 g in 10 mL of water. Stir for 30 s, and pass through a coarse filter. Dilute the filtrate with water to 15 mL, and use the filtrate.
Standard solution: 0.4 µg/mL of ammonium chloride in water
Analysis: To the Sample solution and the Standard solution add 0.3 mL of alkaline mer curic–potassium iodide TS, cap the test tubes, and allow to stand for 5 min.
Acceptance criteria: The Sample solution does not exhibit a more intense yellow color than that of the Standard solution (NMT 4 ppm of ammonia).
• LIMIT OF CHLORIDE
Sample solution: Suspend 0.2 g in 10 mL of water. Stir for 30 s, pass through a coarse filter, and use the filtrate.
Standard solution: 2.3 µg/mL of sodium chloride in water
Analysis: To the Sample solution and 10 mL of the Standard solution add 1 mL of nitric acid and 1 mL of silver nitrate TS, and dilute each solution with water to 40 mL. Allow the solutions to stand for 5 min, protected from light.
Acceptance criteria: When viewed against a dark background, the Sample solution is not more turbid than the Standard solution (NMT 0.007% chloride).
• LIMIT OF SULFATE
Sample solution: Suspend 0.75 g in 15 mL of water. Stir for 30 s, pass through a coarse filter, and use the filtrate.
Standard solution: Add 0.15 mL of 0.020 N sulfuric acid to 15 mL of water.
Analysis: To the Sample solution and the Standard solution add 2 mL of barium chloride TS and 1 mL of 3 N hydrochloric acid, dilute each solution with water to 30 mL, and mix. Allow the solutions to stand for 5 min.
Acceptance criteria: The Sample solution is not more turbid than the Standard solution (NMT 0.02% sulfate).
• ORGANIC IMPURITIES
Solution A: 6.8 g/L of potassium hydrogen sulfate and 3.4g/L of tetrabutylammonium hydrogen sulfate in water. Adjust with 2 N potassium hydroxide to a pH of 6.5.
Solution B: 0.1 g/L of sodium azide solution
Mobile phase: Solution A and Solution B (60:40)
System suitability solution: 0.2 mg/mL each of Adenosine and inosine in Mobile phase
Sample solution: 1.0 mg/mL of Adenosine in Mobile phase
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography <621>, System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 254 nm
Column: 4.6-mm × 25-cm; 5-µm packing L1
Flow rate: 1.5 mL/min
Injection size: 20 µL
System suitability
Samples: System suitability solution
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 9.0 between adenosine and inosine
Tailing factor: NMT 2.5
Relative standard deviation: NMT 2.0%
[NOTE-Chromatograph the Sample solution, and adjust the run time to at least twice the retention time of the major peak.]
Analysis
Sample: Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of each impurity in the portion of Adenosine taken:
Result = (rU/rT) × 100
rU = peak response of each impurity from the Sample solution
rT = sum of all the responses for all peaks from the Sample solution
Acceptance criteria
Individual impurities: NMT 0.1% each of guanosine, inosine, and uridine, and NMT 0.2% of adenine
Total impurities: NMT 0.5%
SPECIFIC TESTS
• MELTING RANGE OR TEMPERATURE <741>: 233°-238°
• OPTICAL ROTATION, Specific Rotation <781S>: -68° to -72°
Test solution: 20 mg/mL in sodium hydroxide solution (1 in 20), determined on a sample previously dried at 105° for 2h
ACIDITY OR ALKALINITY: Suspend 1 g in 20 mL of carbon dioxide-free water. Stir for 30 s, and pass through a coarse filter. To each of two 10-mL portions of the filtrate add 0.1mL of bromocresol purple TS.
Acceptance criteria: NMT 0.3 mL of 0.01 N sodium hydroxide is required to produce a blue-violet color in one portion. NMT 0.1 mL of 0.01 N hydrochloric acid is required to produce a yellow color in the other portion.
•LOSSON DRYING <731>: Dry a sample at 105℃ for 2 h: it loses NMT 0.5% of its weight.
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
•PACKAGING AND STORAGE: Preserve in tight, light-resistant containers, and store at controlled room temperature.
• USP REFERENCE STANDARDS <11>
USP Adenosine RS

Function and Application of Adenosine (CAS: 58-61-7)
1. Adenosine is a protein kinase activators. Improve myocardial hypoxia, coronary artery expansion, increase myocardial contractility, increased cardiac output and other effects for angina pectoris, acute myocardial infarction adjuvant therapy, but its role in maintaining a shorter time. Used to relieve angina and acute and chronic myocardial infarction and other diseases. Adenosine plays a physiological role on the cardiovascular system and the body's many systems and organizations.
2. Adenosine is used in the synthesis adenosine triphosphate, adenosine (ATP), adenine, adenosine, the vidarabine important intermediates. Adenosine mainly used in the pharmaceutical industry for the manufacture of adenosine; adenosine triphosphate; coenzyme and its series of products such as cyclic adenosine phosphate and other drugs as the main raw material.
3. Adenosine plays an important role in biochemistry, including adenosine triphosphate (ATP) or adeno-bisphosphate (ADP) form of transfer of energy, or to cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) for signal transmission and so on. In addition, adenosine is an inhibitory neurotransmitter (inhibitory neurotransmitter), may promote sleep.
4. Adenosine is an amino acid. Studies indicate anti-wrinkle and skinsmoothing capacities. Although little is written about its direct skin benefit, adenosine plays an important role in biochemical processes. As adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and adenosine diphosphate (ADP), it is involved in energy transfer, and as cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) in signal transduction.
5. Adenosine is an antiarrhythmic drug that converts paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia to sinus rhythm. It is used for supraventricular arrhythmias related to atrioventricular.
-
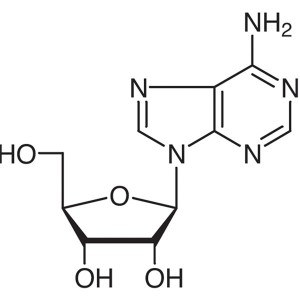
Adenosine CAS 58-61-7 Assay 99.0%-101.0% USP St...
-
Cytidine CAS 65-46-3 Purity ≥99.0% (HPLC) Purit...
-
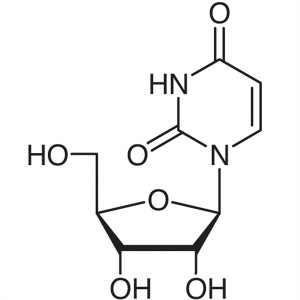
Uridine CAS 58-96-8 Purity ≥99.0% (HPLC) Conten...
-
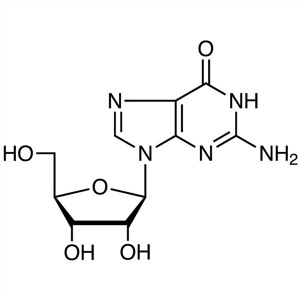
Guanosine CAS 118-00-3 Purity ≥98.0% (HPLC) Ass...
-
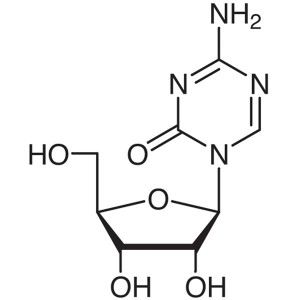
5-Azacytidine CAS 320-67-2 Purity: ≥99.0% (HPLC...
-
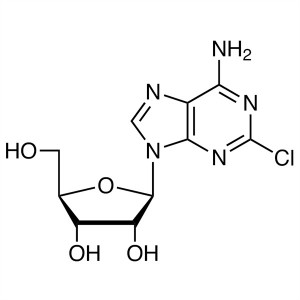
2-Chloroadenosine (2-CADO) CAS 146-77-0 Purity ...
-
2-Aminoadenosine CAS 2096-10-8 Purity ≥99.0% (H...
-
Capecitabine CAS 154361-50-9 Purity 98.0%~102.0...
-
2′-Deoxyadenosine CAS 958-09-8 Purity ≥99...
-
2′-Deoxyadenosine-5′-Monophosphate ...
-
Adenosine 5′-Monophosphate Disodium Salt ...
-
Adenosine 5′-Monophosphate (5′-AMP)...
-
5-Fluorocytidine CAS 2341-22-2 Assay ≥98.0% (HPLC)
-
Cyclocytidine Hydrochloride CAS 10212-25-6 Puri...
-
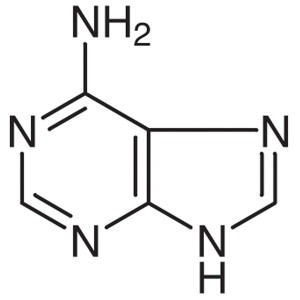
Adenine CAS 73-24-5 Assay 98.0%~102.0% (Titrati...
-
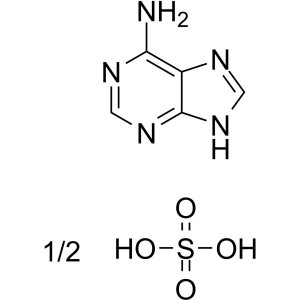
Adenine Hemisulfate Salt CAS 321-30-2 Purity ≥9...